Explore the region
Drag the image to rotate the anatomy
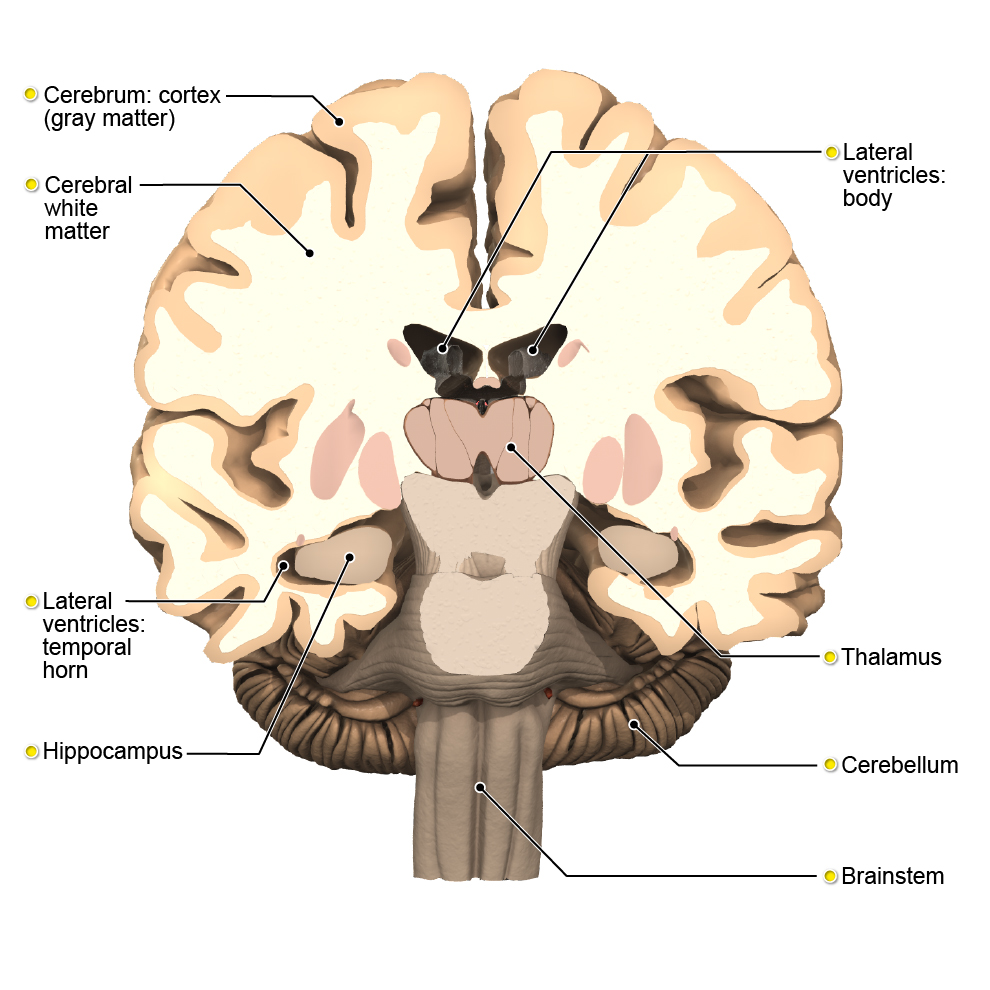
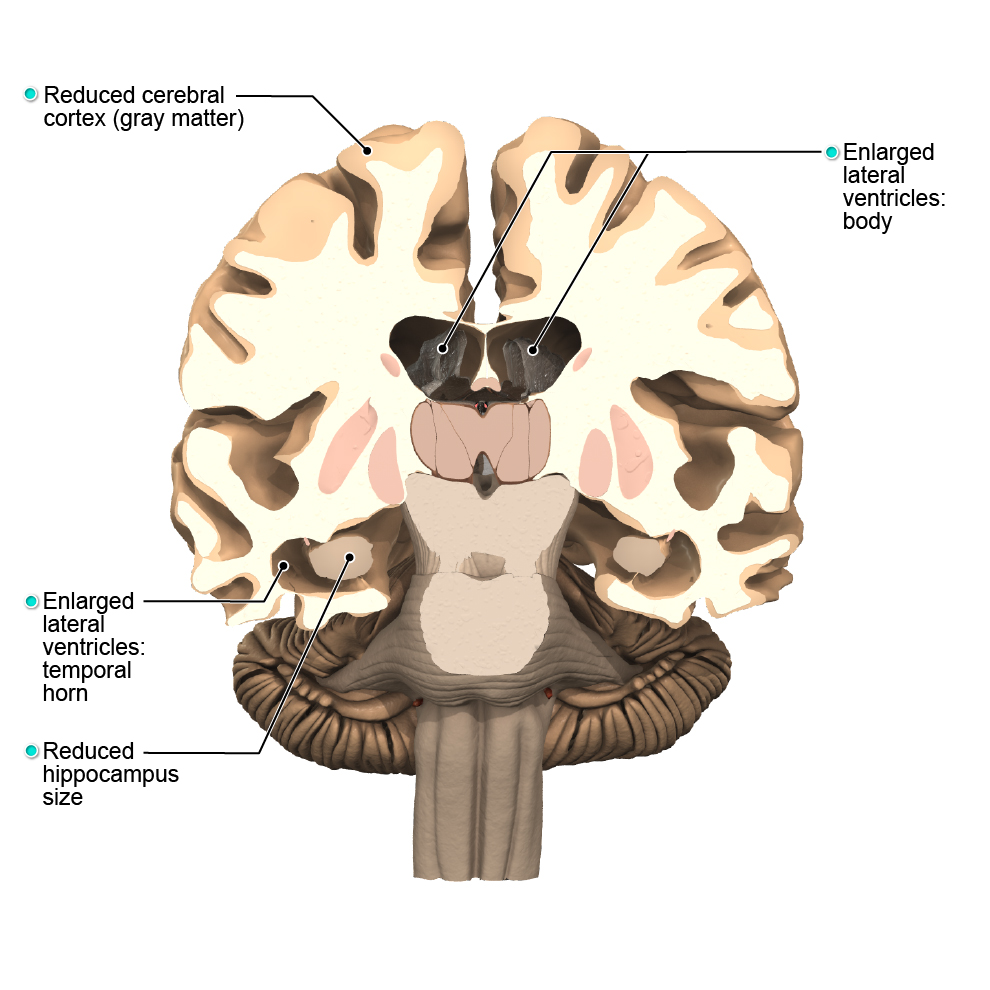
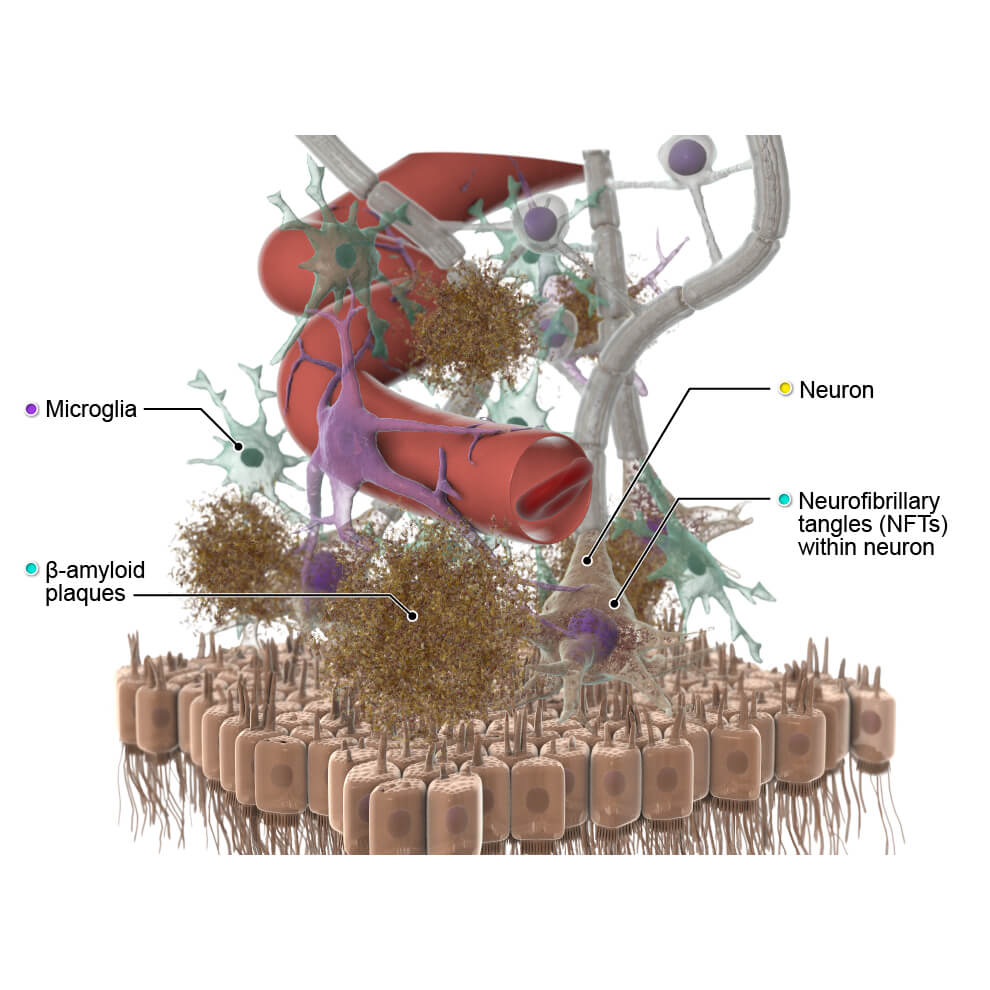
The brain can be divided into four main parts, including the cerebrum, brainstem, diencephalon and the cerebellum.
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes:
- Frontal
- Temporal
- Parietal
- Occipital