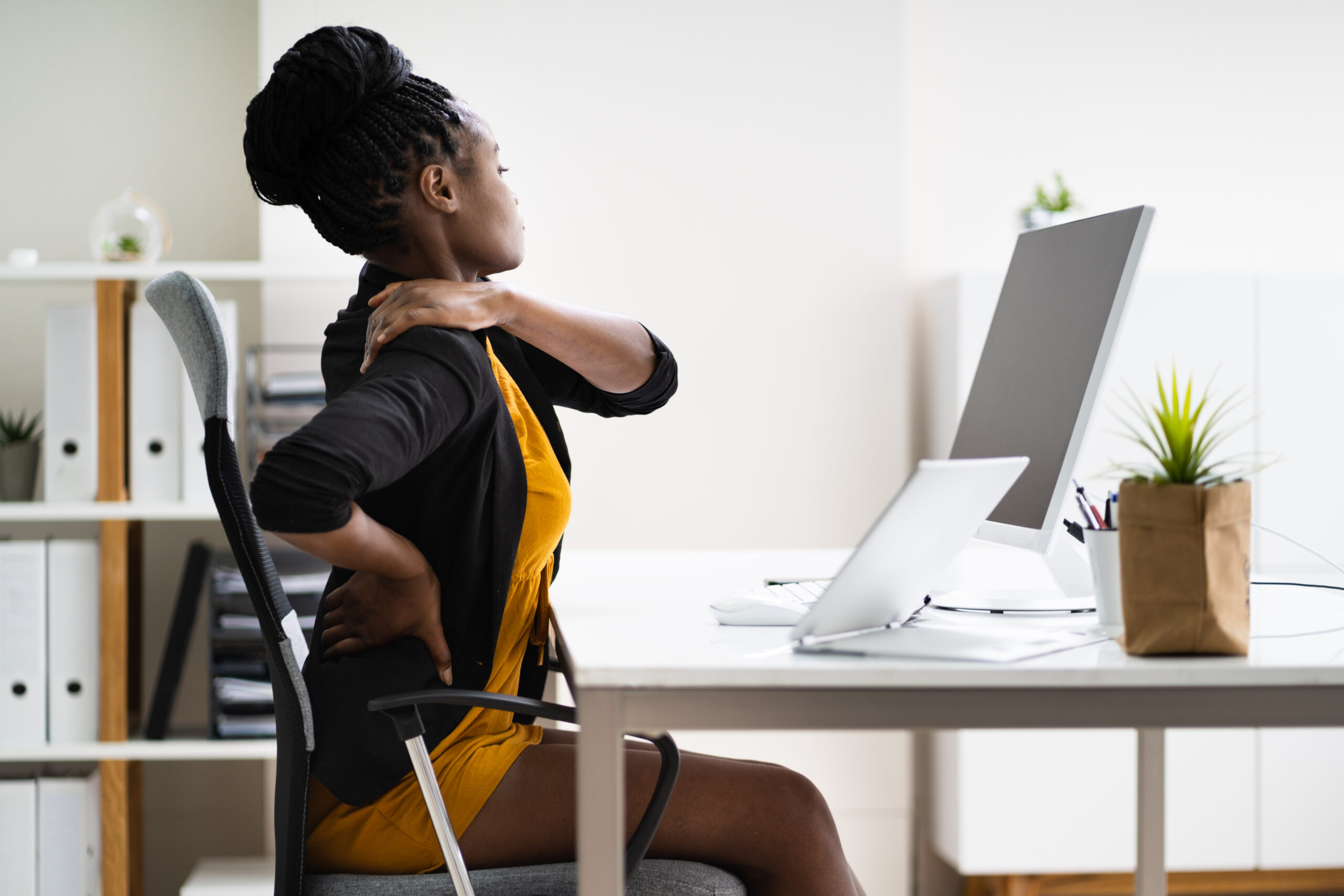
Do you spend many hours each day sitting at a desk, staring at a screen? Have you ever felt an ache in your neck or back while working or studying and wondered why? It’s time to learn more about ergonomic design and how it can help you work in an environment better suited to your anatomy and physiology.
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, more people have the flexibility to work and study at home. While you might like to snuggle on the sofa with your laptop balanced on your lap, sitting in this way for a long time can have a negative effect on your posture and your health. You may already be aware of “good” posture, but still struggle to maintain it for a prolonged period of time because you’re not used to it. This is where ergonomic design can help. It takes health and posture into consideration so you can always work comfortably and prevent injury whether at home or in the office.
What is ergonomically-designed furniture and why is it important?
In a work or study environment, “ergonomic design” refers to a workstation that has been tailored specifically for your needs. Well-designed ergonomic furniture can maximize efficiency and safety in the workplace. This is important as it can boost comfort and productivity, while minimizing work-related injuries.
How to set up your workstation using ergonomics
Everyone is built differently so each workstation must be tailored to the individual. However, the below suggestions are common rules that can be applied for an optimal working environment:
-
- Chair – This is the foundation of your workstation and all other areas must be built around it. Make sure it has good lumbar support for your back or add pillows if needed. Your arms should hang easily by your side, your elbows lightly touching the armrests if the chair has them. Feet should either be firmly on the ground or on a footrest.
- Lighting – Your desk should face 90 degrees from a window to avoid glare or use curtains to cover the light. Overhead light should be kept low and remember to use the 20-20-20 rule: Twenty minutes of work followed by 20 seconds of rest while your eyes focus on something 20 feet away.
- Screen – Your eyes should be level with the top of your screen, and the keyboard should sit an arm’s length away. If working on a laptop, it’s ideal to have a separate keyboard and mouse so the screen can be the right height for you. If the screen is too far away, even while wearing glasses, then enlarge the text to prevent eye strain.
- Work surface – Desk height should be low enough so that when you’re typing your elbows are extended more than 90 degrees, thereby increasing blood flow to your wrists. If you find yourself leaning your elbow/wrists/hands on any surface for too long, consider either a padded wrist rest or a padded mouse mat. The mouse should be as close to the keyboard as possible, and the keyboard should be aligned with your body so the ‘H’ is always in the middle.
Don’t forget, if you feel discomfort or sluggish then it might be time to take a break. Don’t rush to complete a task if your body is feeling achy. Try and focus on what you can do to make yourself feel better, your brain and body will thank you!
What happens to your body in a poor ergonomic environment?
If your workstation is incorrectly set up, you might notice discomfort from sitting still for long periods or you might feel constant twinges even when not working. So, which parts of your anatomy does it affect and how can you improve it?
Spine
Your spine helps with keeping your body upright and movement. It is usually made up of 33 vertebrae (back bones) on average, however some fuse as we grow. Hence, adults only have 26 vertebrae in average on average. The spine can be divided into five regions – cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccyx. Each region can perform a range of motion, such as flexion (bending). The facet joints have cartilage that allows the vertebrae to slide against each other while performing the movements, while the intervertebral discs act as a cushion between the vertebrae.
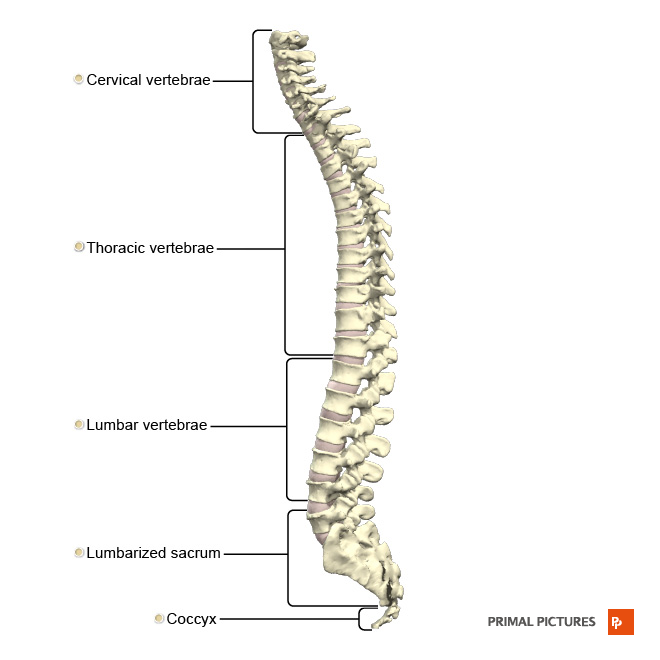
Being hunched over your computer results in bad posture, as your neck is leaning forward and not resting directly above your shoulders. Prolonged exposure to bad posture adds stress to the spine – as well as the surrounding muscles, ligaments and intervertebral discs – when they try to overcompensate for the imbalance. As a result, you may feel neck, back and shoulder pain. You may even end up with serious clinical conditions such as disc hernia and text neck (check out our “text neck” blog post). For prevention, you could invest in a chair designed for long periods of sitting like a gaming chair with excellent lumbar support, a comfortable seat and armrests.
Eyes
Your eyes are made up of several different structures that allow you to see. The cornea, the transparent dome that covers the eye, helps focus light onto the retina. The iris controls the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil. It is important that these structures stay moist. Hence, every time you blink, tiny tears are released from the tear gland, also known as the lacrimal gland, to coat your eyes and clean any debris.
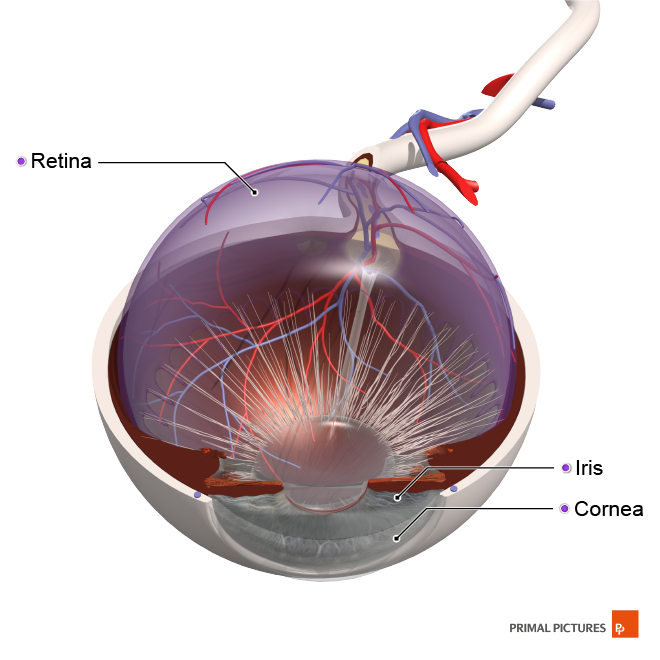
Staring at a screen for several hours a day can cause computer vision syndrome (CVS) or eye strain. This can result in headaches, blurred vision, dry eyes and neck and shoulder pain due to leaning forward to see the screen clearly. Poor lighting and having the screen at the wrong angle (too high for the eyes) can also result in CVS. To alleviate this, you can use dimmer lights and angle screens away from windows (or use a blind) to avoid glare. Again, make sure you are sitting properly so the screen is positioned a good distance from your eyes and remember to blink often and follow the 20-20-20 rule as mentioned above. And don’t forget to take regular breaks.
Wrist joint
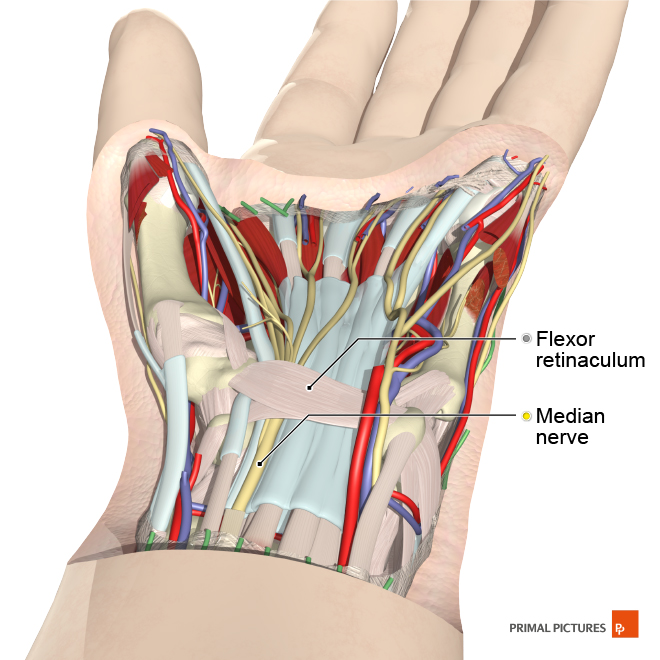
The wrist is a joint made up of a complex series of bones, including the eight carpal bones that link the hand to the forearm. This joint allows a wide variety of movement: It can bend, straighten, move laterally and rotate, which also makes it prone to injury.
Repetitive stress to the wrist, such as using a flat shaped mouse for a prolonged time, can cause carpal tunnel syndrome. This is where the strong connective tissue band that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel, called the flexor retinaculum, becomes inflamed and compresses the median nerve and muscle tendons that pass through it. This results in pain, however it can be relieved by using an ergonomic mouse which keeps your hand in a neutral position.
Cardiovascular system
The cardiovascular system encompasses the heart, blood vessels and blood. The core function of the heart is to maintain blood flow throughout the body and is critical for us to survive.
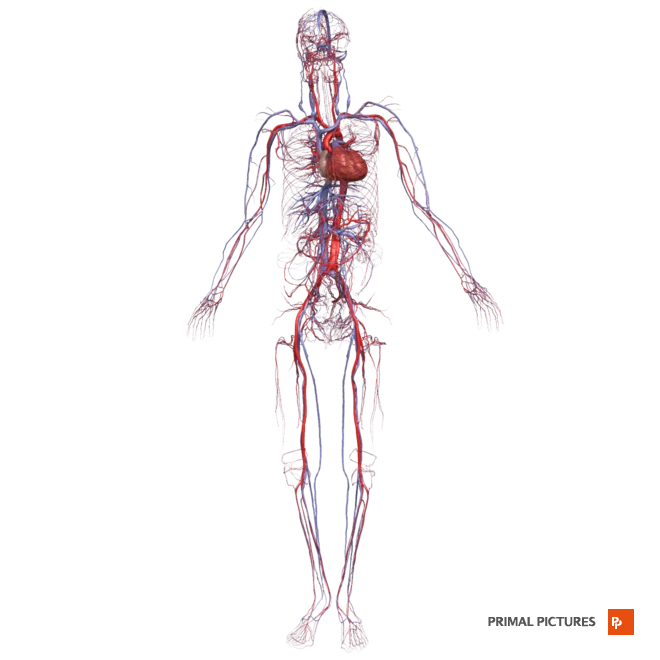
Sitting for long periods of time decreases blood flow around your body, which can potentially increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer. It can also lead to obesity, high blood pressure and unhealthy cholesterol levels.
A good way to combat these issues is to take regular breaks, so remember to get up and move around. Where possible, invest in a standing desk or stack your computer to a height where you need to stand and shift your weight while working. Anything to get your body moving again will help lower blood pressure and could even help with losing some excess weight!
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs)
If you ignore the warnings from your body and continue working in a poorly ergonomically designed environment, then you could develop a work-related musculoskeletal disorder (MSD). This includes any injury that can be attributed to the workplace, such as those affecting muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves or blood vessels. It can occur through exposure to heavy lifting, pushing or pulling heavy loads, lifting items overhead or bending. In an office environment it can be caused by un-ergonomically designed workstations as mentioned above, which can encourage sitting incorrectly and problematic repetitive motions.
According to the UK’s Health and Safety Executive (HSE), 6.9 million workdays were lost due to MSDs in just one, pre-Covid year in the country. And a 2021 World Health Organization study found that globally nearly 90 million disability-adjusted life years were estimated to be attributable to the workplace each year. Having a MSD can lead to constant pain, limited mobility and dexterity, decreased well-being, feeling unable to participate in society and early retirement.
It may be tempting to work long hours without taking breaks, but always be mindful of uncomfortable signs and signals from your body. Better ergonomic workstation design and avoiding long periods without flexing your entire body is always better for your health – and could likely boost productivity as well.
The images used in this piece have been taken from Primal’s 3D Atlas. To learn more about this or other Primal learning resources – please fill in the form here and our team will be in touch.
